2. Background#
2.1. What is GenAI? How does it work?#
This section needs expanding. It can reuse the content of one of our past staff training’s events:
Glerean, E., & Silva, P. E. S. (2024, March 28). Artificial Intelligence and Research Work. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10890289
2.2. Background literature#
Note
In this page a very short literature review on the use of artificial intelligence in qualitative research
Warning
This is not a systematic literature review! I would be happy to join forces and conduct a systematic literature review, please get in touch.
While the popularity of GenAI tools, such as ChatGPT, has increased over the past months, using AI – or more specifically machine learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NPL) techniques – is nothing new in the field of qualitative research and, more broadly, any type of research that is dealing with text as its main form of input.
However, if we limit the scope of our background literature to recent studies that looked at the use of GenAI and qualitative analysis methods, it is important to mention:
Zhang, H., Wu, C., Xie, J., Lyu, Y., Cai, J., & Carroll, J. M. (2023). Redefining qualitative analysis in the AI era: Utilizing ChatGPT for efficient thematic analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.10771. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.10771.pdf
Tip
If you have no time for anything else, just read Zhang et al. 2023 linked above.
The study by Zhang et al. considers the framework of Thematic Analysis, and collected data from participants on various aspects of using ChatGPT for helping in the qualitative analysis process. The paper has important considerations on the research integrity aspects of using GenAI since “Reading, understanding, and evaluating ChatGPT results uses no less time than the original workflow” as well as privacy concerns. Section 6 is particularly useful as it proposes a framework for ChatGPT prompts for thematic analysis.
Note
What is a prompt? In the context of LLMs and GenAI, the inference process – the process that loads the model data (weights) to perform token-by-token synthesis – needs to be prompted so that it continues the previous sentence by repetitively adding tokens in a controlled way, but with a certain level of randomness (temperature). The prompt is then the sentences that you might be writing in a chat interface.
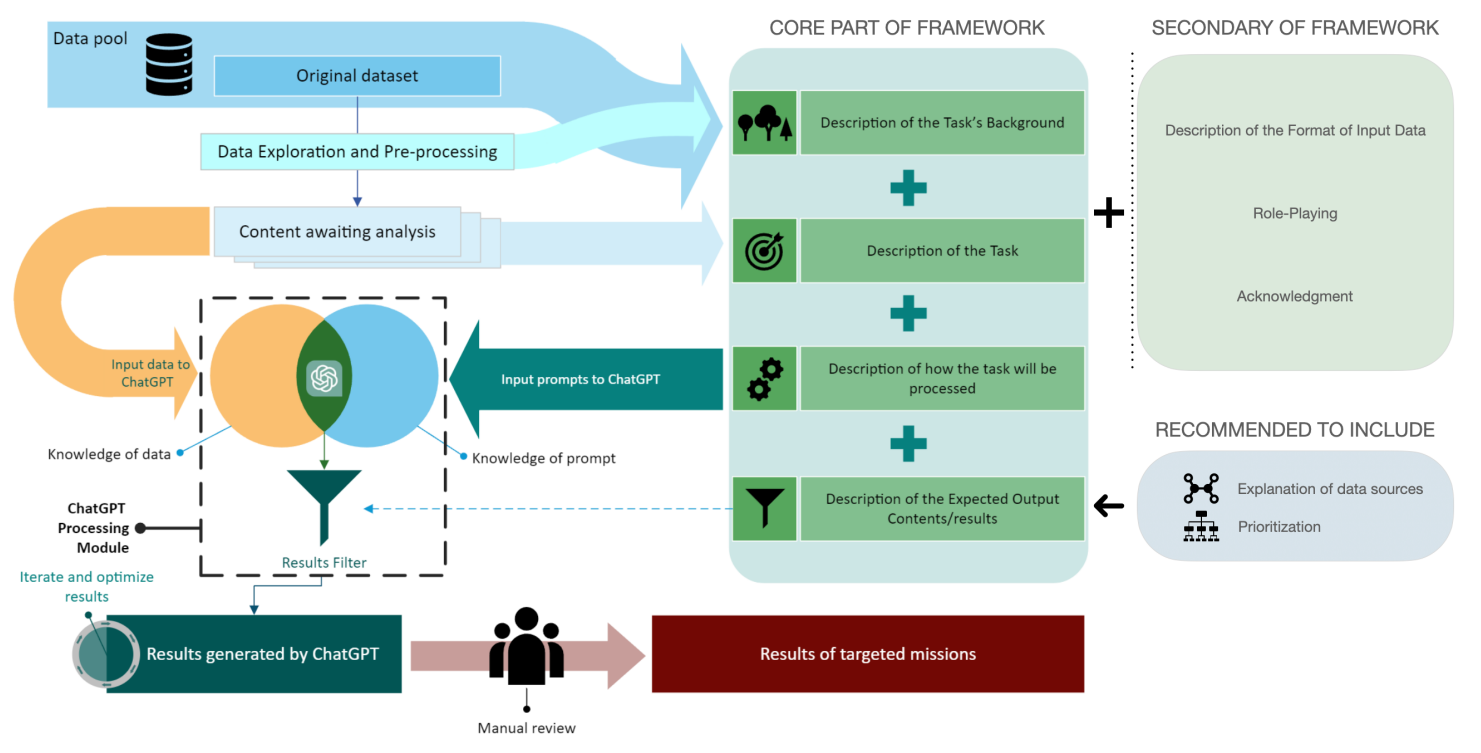
Prompt design for qualitative analysis, by Zhang et al. 2023#
Warning
This section needs to be expanded with some more recent literature. Get in touch to help!
